Audiometers are medical diagnostic devices used in hearing testing to assess and evaluate hearing loss and hearing ability. These devices play an important role for audiologists, otolaryngologists and other health professionals in the diagnosis, treatment and monitoring of hearing loss.
When evaluating the results of audiometers, the audiologist takes into account hearing thresholds, possible asymmetry between auditory nerves, speech understanding and other important audiological parameters. Based on the results, the extent and type of hearing loss is determined and, if necessary, an appropriate treatment plan is developed for the patient.
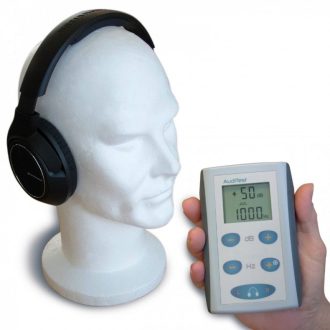
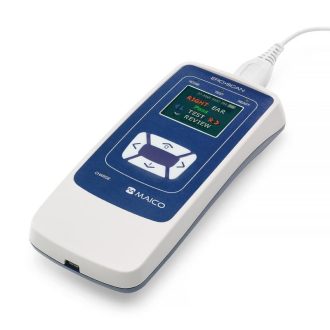
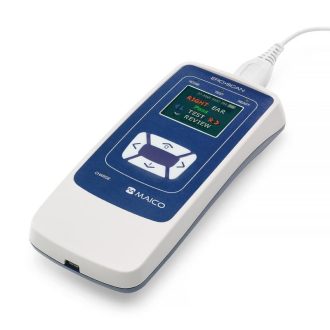
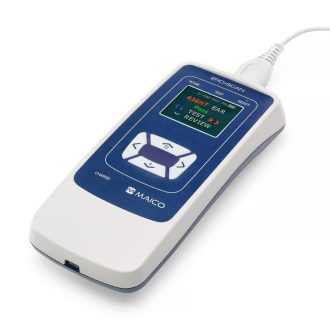
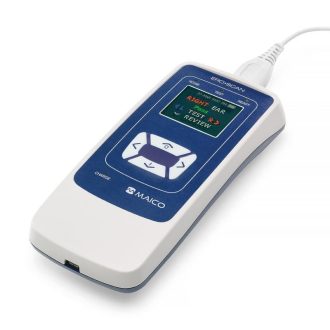
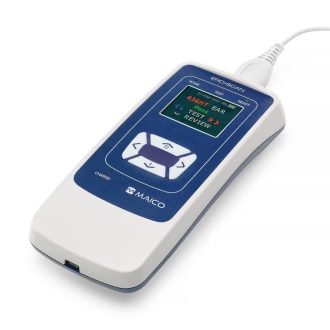
AudiScan handheld audiometer
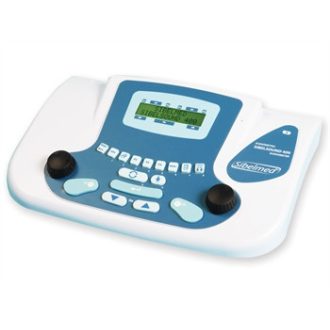
SA-7 portable audiometer
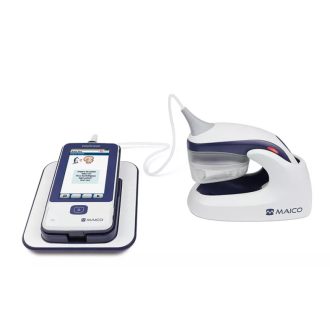
BSA-1 infant audiometer
Patient feedback for SA-7 scanning audiometer
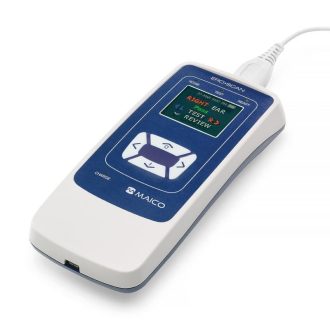
touchTymp MI 26 audiometer with printer | with race car function
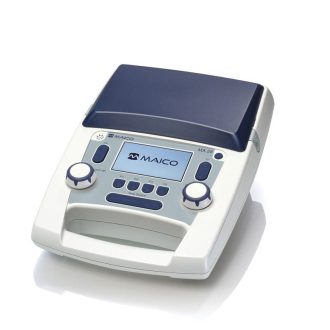
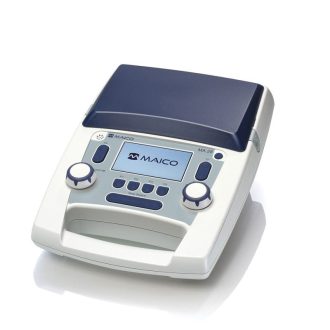
MA 28 Screening Audiometer with bone conduction (MA 28 BC)
Pilot Test - audiometer for children
Eroscan Screener screener combo | with printer
MA 28 Screening Audiometer with standard equipment (MA 28)
Eroscan Screener screener combo | without printer
touchTymp MI 26 audiometer with printer | without race car function
touchTymp MI 26 audiometer without printer | without race car function
touchTymp MI 26 audiometer without printer | with race car function
Sibelsound 400-AOM audiometer with W50 software - air+bone+masking
Sibelsound 400-supra audiometer - air+bone+software
Maico easyScreen BERAphone® (ABR) csecsemő hallásvizsgáló készülék
Audiometers are medical diagnostic devices used in hearing testing to assess and evaluate hearing loss and hearing ability. These devices play an important role for audiologists, otolaryngologists and other health professionals in the diagnosis, treatment and monitoring of hearing loss.
When evaluating the results of audiometers, the audiologist takes into account hearing thresholds, possible asymmetry between auditory nerves, speech understanding and other important audiological parameters. Based on the results, the extent and type of hearing loss is determined and, if necessary, an appropriate treatment plan is developed for the patient.